PRP Therapy and Fertility
Recently, PRP has emerged as a potential option in fertility treatments, particularly for women undergoing Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
PRP Therapy and Fertility
Introduction to PRP
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is gaining recognition for its regenerative and healing properties, initially celebrated in sports medicine and cosmetic procedures. Recently, PRP has emerged as a potential option in fertility treatments, particularly for women undergoing Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). This article dives into what PRP therapy is, its applications in fertility, and considerations if you're exploring this option on your fertility journey.
What is PRP?
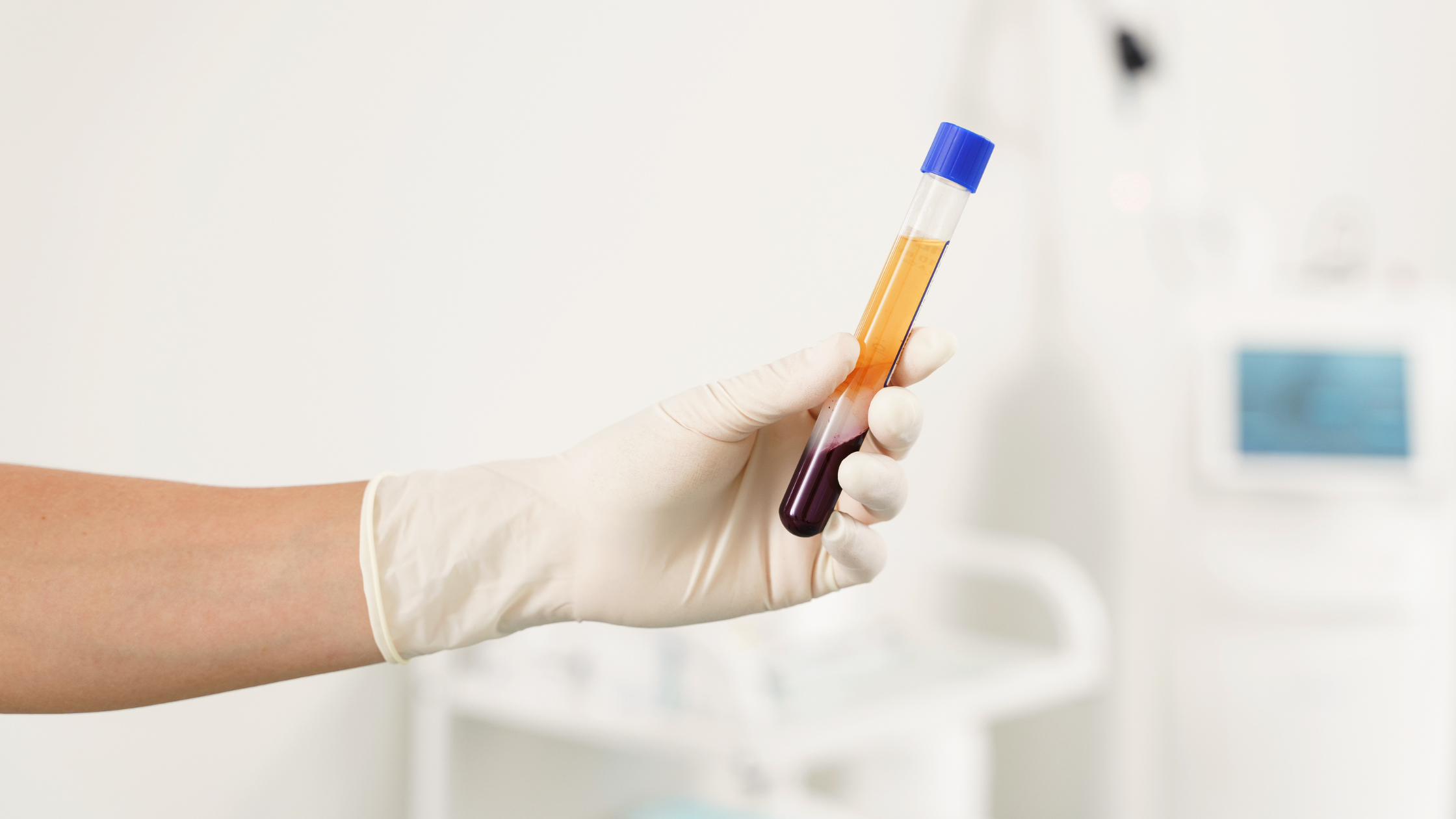
PRP therapy utilizes a concentrated form of your blood's platelets, which are rich in growth factors that promote tissue repair and regeneration. The process involves:
Blood Collection: A sample of your blood is drawn, typically from your arm.
Centrifugation: This blood is then spun in a centrifuge to separate the plasma, which contains a high concentration of platelets, from the other blood components.
Injection: The platelet-rich plasma is injected into the targeted area to stimulate healing and growth.
These growth factors released by the platelets play a crucial role in cellular repair and regeneration, making PRP a valuable tool in various medical fields, including fertility treatments.
PRP in Fertility Treatments: IUI and IVF
PRP therapy is being integrated into fertility treatments with promising results. For women facing challenges in conceiving, PRP offers potential benefits in improving egg quality and quantity and enhancing the uterine lining. In the context of IUI and IVF, PRP therapy can play a crucial role:
IUI: PRP can enhance the quality and quantity of eggs, providing a better pool for insemination. It can also improve the uterine lining, creating a more conducive environment for the sperm to meet the egg and for the embryo to implant.
IVF: PRP’s role in improving egg quality and quantity is vital. During IVF, having higher-quality eggs can lead to better embryo quality. Additionally, enhancing the uterine lining's thickness and receptivity can significantly increase the chances of successful embryo implantation and pregnancy.
Research from PMC shows that following PRP therapy, women with thin endometrium showed an increase in endometrial thickness and increased pregnancy rates. Additionally, “in women with poor ovarian reserve, autologous intraovarian PRP therapy increased anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) levels and decreased follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), with a trend of increasing birth rates. This trend was also noted in women with recurrent implantation failure.”₁
Here’s how PRP is often applied in fertility treatments like IUI and IVF:
Improving Egg Quality and Quantity:
Ovarian Rejuvenation: PRP can be injected into the ovaries to potentially stimulate the growth of higher-quality eggs. This is particularly beneficial for women with diminished ovarian reserve or those who have not responded well to traditional fertility treatments. PRP’s growth factors may help rejuvenate ovarian tissue, increasing the chances of producing viable eggs for fertilization.
Follicular Activation: For women experiencing early ovarian aging or poor ovarian response, PRP injections can activate dormant follicles, potentially increasing the number of eggs available during an IVF cycle. This can improve the chances of retrieving a sufficient number of eggs to create healthy embryos.
Enhancing Uterine Lining Thickness
Endometrial Receptivity: A thick and receptive uterine lining is crucial for successful embryo implantation. For women with a thin or unresponsive endometrium, PRP injections directly into the uterine lining can promote growth and improve its quality. This is particularly important during an IVF cycle, where a receptive endometrium is necessary for the embryo to implant and thrive.
Recurrent Implantation Failure (RIF): Women who have experienced multiple failed IVF cycles due to recurrent implantation failure may benefit from PRP therapy. By enhancing the endometrial environment, PRP can increase the likelihood of successful implantation and reduce the risk of another unsuccessful cycle.
What to Expect from PRP Therapy & Fertility Treatments
If you’re considering PRP as part of your fertility treatment plan, here’s what to anticipate:
Consultation and Preparation: Your fertility specialist will assess your medical history and fertility challenges to determine if PRP is suitable for you. If you proceed, a blood sample will be taken to prepare the PRP.
Procedure: The prepared PRP is injected either into the ovaries or the endometrium, depending on the treatment goal. The procedure is minimally invasive and typically done on an outpatient basis.
Post-Procedure Care: Following the PRP injection, you may experience mild discomfort or spotting, but these symptoms usually resolve quickly. Your doctor will provide specific aftercare instructions to ensure optimal recovery and effectiveness.
Safety and Considerations of PRP When Trying to Conceive
PRP therapy is generally safe since it uses your own blood, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions or infections. However, there are important considerations to keep in mind:
Minimal Risk: The use of autologous (self-derived) blood in PRP significantly reduces the risk of adverse effects. Some patients may experience minor pain or discomfort at the injection site, but serious complications are rare.
Experimental Nature: PRP in fertility treatments is still considered experimental and is not yet widely available at all fertility clinics. This means that while initial results are promising, more research is needed to establish its long-term safety and efficacy fully.
Consultation with Specialists: It’s essential to discuss with your fertility specialist how PRP fits into your overall treatment strategy. They can provide insights into its potential benefits and whether it’s a suitable option for your specific fertility challenges.
Key Considerations for Fertility Patients
Before deciding to include PRP therapy in your fertility treatment, consider the following:
Research and Expectations: Approach PRP with realistic expectations. While it shows promise, it is not a guaranteed solution for everyone, and its effectiveness can vary. Understanding what PRP can and cannot do will help you make an informed decision.
Cost Implications: PRP treatments can be costly and are often not covered by insurance, especially when used for fertility purposes. Discuss the financial aspects with your clinic and explore any payment plans or financing options available.
Integration with Other Treatments: Talk to your fertility specialist about how PRP therapy will integrate with your current treatment plan, particularly if you’re undergoing IUI or IVF. Understanding how PRP complements other treatments is crucial for optimizing your chances of success.
Procedure Frequency: Depending on your individual case, multiple PRP sessions might be necessary. Your doctor will advise you on the recommended frequency and timing of these treatments to maximize their effectiveness.
Support and Mental Health: Fertility treatments can be emotionally taxing. Ensure you have a solid support system and access to mental health resources to navigate the emotional ups and downs of your journey.
PRP therapy represents an exciting development in fertility treatments, offering hope for many women facing challenges in conceiving. Whether you're looking to improve egg quality and quantity, enhance endometrial receptivity, or overcome recurrent implantation failure, PRP’s regenerative properties provide a promising option to explore. However, it’s essential to work closely with your fertility specialist to determine if PRP is the right choice for you.
References:
Sharara, F. I., Lelea, L., Rahman, S., Klebanoff, J. S., & Moawad, G. N. (2021). A narrative review of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in reproductive medicine. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, 38(5), 1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-021-02146-9
Medical Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your healthcare provider or qualified medical professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this blog.